Hyperthyroidism is a sneaky condition that can affect cats of all ages. It occurs when the thyroid gland goes into overdrive and produces too much hormone, causing a range of symptoms that can make your feline friend feel downright miserable. From weight loss to hyperactivity and vomiting, these symptoms can take a toll on your cat’s health if left untreated.
So, how do you treat hyperthyroidism in cats? Luckily, there are several options available to help manage this condition and improve your cat’s quality of life. In this article, we’ll delve into the different ways to treat hyperthyroidism in cats and weigh the pros and cons of each method.
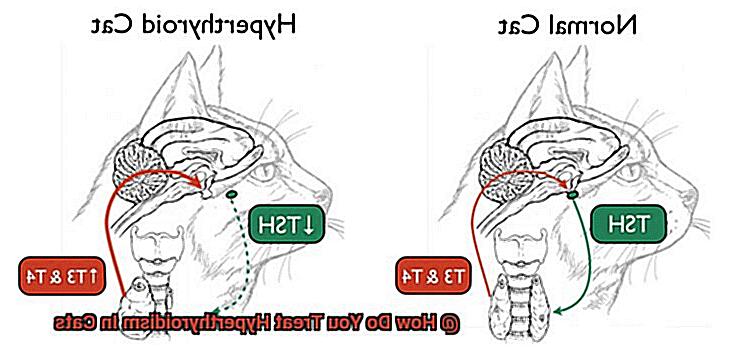
One of the most popular treatments for feline hyperthyroidism is medication. This option involves giving your cat pills or liquid medicine to regulate their thyroid hormone levels. Another option is radioactive iodine therapy, where a small amount of radioactive iodine is injected into your cat’s bloodstream to destroy overactive thyroid tissue. Surgery is also an option but usually reserved for cases where medication and radioactive iodine therapy have not been successful or are not viable treatment options.
If you suspect that your furry friend has hyperthyroidism or have already received a diagnosis, don’t delay in seeking treatment. Early intervention can prevent further complications and provide your cat with the best possible outcome. With proper care and attention, your cat can live a happy and healthy life despite this pesky condition.
What is Hyperthyroidism in Cats?
However, sometimes health issues can arise, including hyperthyroidism, a common endocrine disorder in cats. This condition occurs when the thyroid gland, located in the neck, becomes overactive and produces too many thyroid hormones.
Hyperthyroidism can cause a variety of symptoms that may not necessarily indicate this disorder, such as weight loss despite an increased appetite, vomiting, diarrhea, excessive thirst and urination, and hyperactivity. Therefore, consulting with a veterinarian is crucial if you notice any of these signs.
While the exact cause of hyperthyroidism in cats is not always clear, it is more commonly seen in older cats and certain breeds such as Siamese and Himalayans. Environmental toxins and dietary factors may also play a role.
Fortunately, several effective treatment options are available for hyperthyroidism in cats. Medication can help regulate the production of thyroid hormones and can be administered orally or transdermally. This approach is often effective in controlling hyperthyroidism symptoms.
Another treatment option is radioactive iodine therapy, which involves injecting a small dose of radioactive iodine into the cat’s bloodstream. While highly effective with a high success rate, it requires special facilities and can be costly.
Surgery to remove the affected thyroid gland is also an option for treating hyperthyroidism. However, surgery carries some risks and may not be suitable for all cats.
In addition to these conventional treatment options, alternative therapies such as dietary changes focusing on low-iodine foods, acupuncture, herbal supplements, and homeopathic remedies may be beneficial for managing hyperthyroidism symptoms. Nevertheless, it’s essential to consult with your veterinarian before trying any alternative therapies to ensure they are safe and effective for your cat.
Symptoms of Hyperthyroidism in Cats
But when your cat starts exhibiting unusual behaviors such as losing weight despite having a good appetite or vomiting frequently, it’s time to pay attention. These signs could indicate hyperthyroidism, a prevalent endocrine disorder in cats.
Hyperthyroidism occurs when the thyroid gland produces too much thyroid hormone, which controls the cat’s metabolism. The excess hormone production can lead to various symptoms that can go unnoticed for a while. However, as the disease progresses, the symptoms become more pronounced and severe.
One common symptom of hyperthyroidism in cats is weight loss. Despite having a good appetite, your cat may be losing weight because their increased metabolic rate burns more calories than they can consume. Additionally, hyperthyroid cats may experience an increase in appetite, thirst, and urination.
Gastrointestinal problems such as vomiting and diarrhea are also common among hyperthyroid cats. The disease can also affect the heart and cause hypertension (high blood pressure), which can lead to heart failure or stroke. Your cat may also exhibit behavioral changes such as restlessness, anxiety, or aggression.
It’s crucial to recognize the symptoms of hyperthyroidism in cats early on so that treatment can begin promptly. If you notice any of these symptoms in your cat, seek veterinary care immediately. The good news is that several effective treatment options such as medication, radioactive iodine therapy, and surgery are available to help regulate the production of thyroid hormones and manage these symptoms.
Treatment Options for Hyperthyroidism in Cats
There are various treatment options available to treat this common condition in cats. In this article, we’ll explore the different treatment options available for hyperthyroidism in cats and their unique advantages and disadvantages.
Medication
If your feline friend has been diagnosed with hyperthyroidism, don’t lose hope. Medication can be an effective treatment option that could help them get back to their old selves. Methimazole is the most commonly used medication for treating this condition in cats. By reducing the amount of thyroid hormone produced by the thyroid gland, it helps to control the overactive thyroid cells.
Methimazole can be administered orally in tablet form or as a transdermal gel, but it’s important to note that this medication does come with some risks. Cats may experience side effects such as vomiting, diarrhea, and loss of appetite. More serious side effects such as liver damage or bone marrow suppression are also possible. That’s why it’s crucial to monitor your cat closely while they’re on this medication and consult with a veterinarian if any adverse reactions occur.
Another option worth considering is radioactive iodine therapy. This treatment involves injecting a small amount of radioactive iodine into your cat’s bloodstream, which is then absorbed by the thyroid gland. The radiation destroys the overactive thyroid cells, reducing the amount of thyroid hormone produced.
While radioactive iodine therapy is highly effective and generally well-tolerated by cats, it does require hospitalization and isolation for a period of time due to the radioactivity. However, it can provide a cure for hyperthyroidism.
Remember to consult with your veterinarian to determine the best course of action for your cat’s individual needs. Methimazole may be sufficient for some cats, while others may require radioactive iodine therapy. Whatever treatment option is chosen, it’s essential to monitor your cat closely and seek veterinary care if any concerning symptoms arise.
Radioactive Iodine Therapy
If your furry friend has been diagnosed with feline hyperthyroidism, you may be wondering which treatment option is right for them. Allow me to introduce you to the gold standard treatment for this condition – radioactive iodine therapy.
This highly effective one-time treatment uses a radioactive form of iodine that specifically targets and destroys overactive thyroid tissue while preserving healthy tissue. And the best part? It has a success rate of over 95%, making it an excellent choice for treating hyperthyroidism.
Not only is radioactive iodine therapy highly effective, but it is also a safer option for older cats or those with underlying health conditions as it does not require surgery or anesthesia. Additionally, it has minimal side effects compared to other treatments such as medication, which can cause liver or kidney damage.
It’s important to note that while radioactive iodine therapy is highly effective, it may not be suitable for all cats. Cats with severe kidney disease or other medical conditions may not be able to undergo this treatment due to the risk of exacerbating their condition. It’s crucial to discuss all treatment options with your veterinarian before deciding on a course of action.
If your cat does undergo radioactive iodine therapy, they will need to be hospitalized in a special isolation ward for several days to prevent any radiation exposure to humans or other animals. After a week or so, your cat can be discharged and will continue to excrete small amounts of radiation for a few more weeks.
Surgery
Surgery involves the removal of the affected thyroid gland or glands and is usually recommended for cats with large or multiple thyroid nodules that cannot be managed with other treatment methods.
The surgical procedure, known as a thyroidectomy, is performed under general anesthesia, and the cat is monitored during their hospital stay to ensure a smooth recovery. Although surgery can be effective in curing hyperthyroidism, it comes with some risks.
One risk is damage to the parathyroid glands located near the thyroid glands, which regulate calcium levels in the body. Additionally, bleeding during surgery and the possibility of cats developing hypothyroidism if both glands are removed are potential complications.
Despite the risks, surgery can offer a permanent cure for hyperthyroidism and eliminate any need for lifelong medication. This makes it an attractive option for younger cats or those with no underlying health issues.
If you’re considering surgery as a treatment option for your cat’s hyperthyroidism, it’s essential to discuss all benefits and risks with your veterinarian. Your vet will review your cat’s medical history and overall health to recommend the best course of action.
Alternative Therapies for Hyperthyroidism in Cats
While conventional treatments for hyperthyroidism in cats such as medication, surgery, and radioactive iodine therapy have been proven effective, alternative therapies are gaining popularity among those seeking more natural and holistic options.
One promising alternative therapy for hyperthyroidism in cats is acupuncture. This practice involves the insertion of thin needles into specific points on the body, stimulating nerve endings and promoting healing. Besides targeting the thyroid gland, acupuncture has also been shown to improve overall health and well-being in cats.
Another alternative therapy that can help reduce thyroid hormone levels in cats is herbal supplements. Certain herbs like bugleweed, lemon balm, and motherwort have anti-thyroid properties that can aid in treating hyperthyroidism. However, it’s essential to work with a veterinarian or holistic practitioner when using herbal supplements to avoid potential side effects and interactions with other medications.
Dietary changes can also be an effective alternative therapy for hyperthyroidism in cats. A low-iodine and high-protein diet can help reduce thyroid hormone levels while providing essential nutrients for your furry friend’s health. Consider feeding your cat a raw or homemade diet as commercial diets can contain high levels of iodine and other harmful ingredients.
Other alternative therapies for hyperthyroidism in cats include homeopathy, chiropractic care, and massage therapy. While these treatments haven’t been extensively studied for their effectiveness in treating hyperthyroidism, they can offer additional benefits alongside traditional treatments.
It’s crucial to consult with a veterinarian or holistic practitioner before trying any alternative therapies as they can interact with other medications and have potential side effects. Alternative therapies should complement traditional treatments rather than replace them entirely.
Considerations Before Starting Treatment
However, before starting treatment for hyperthyroidism in cats, there are several critical considerations that you should keep in mind.
One of the primary factors to consider is your cat’s age. Hyperthyroidism typically affects older cats, and treatment options may vary depending on their age. Older cats may have underlying health conditions that require attention before starting treatment.
Besides age, the overall health of your cat is also crucial to consider. Hyperthyroidism can lead to complications such as heart disease, high blood pressure, and kidney disease. Therefore, treatment options may need to be adjusted or closely monitored to ensure your cat’s well-being is not compromised.
The severity of your cat’s hyperthyroidism is another crucial factor to consider. Mild or moderate cases may respond well to medication, while severe cases may require more aggressive treatments like surgery or radioactive iodine therapy.
Finally, it’s essential to think about your cat’s lifestyle and your own lifestyle as their owner. Certain treatment options may require frequent vet visits or monitoring while others require isolation for a specific period. These factors should be taken into consideration when deciding on a treatment plan.
Monitoring Your Cat’s Progress After Treatment
Treating hyperthyroidism in cats is a vital step, but it’s equally important to monitor your cat’s progress after treatment to ensure its health is improving.
The first step in monitoring your cat’s progress is to schedule regular follow-up appointments with your veterinarian. During these appointments, your vet will perform a thorough examination, take blood samples, and perform thyroid hormone level tests to determine if the treatment is working or if any adjustments need to be made.
However, monitoring your cat’s progress doesn’t stop at the vet’s office. You should also keep an eye out for common signs of hyperthyroidism such as increased appetite, weight loss, restlessness, thirst, and increased urination. After treatment, these symptoms should start to improve, and your cat should return to its normal activity level. Observing and noting any changes in behavior or symptoms can help you understand how well the treatment is working.
It’s also essential to monitor your cat’s appetite and weight closely during this time. A decrease in appetite or rapid weight loss may be a sign that the hyperthyroidism has not been fully treated or that there is an underlying issue that needs to be addressed.
Finally, following the medication and dietary restrictions prescribed by your veterinarian is crucial. Skipping doses or failing to follow dietary restrictions can hinder the effectiveness of the treatment and delay your cat’s recovery.
Conclusion
If your cat is suffering from hyperthyroidism, you’re not alone. This condition affects many feline friends and can cause a range of unpleasant symptoms like weight loss, vomiting, and restlessness. But the good news is that there are several treatment options available to help manage this condition and improve your cat’s quality of life.
One common treatment method involves medication, which can regulate your cat’s thyroid hormone levels through pills or liquid medicine. Another option is radioactive iodine therapy, where a small amount of radioactive iodine is injected into your cat’s bloodstream to destroy overactive thyroid tissue. Surgery may be considered in severe cases where other treatments have not been successful.
If you prefer alternative therapies, acupuncture, herbal supplements, and low-iodine diets can also be helpful for managing hyperthyroidism symptoms. However, it’s essential to consult with your veterinarian before trying any alternative therapies to ensure they are safe and effective for your furry friend.
Before starting any treatment plan for hyperthyroidism in cats, it’s crucial to consider factors such as their age, overall health, and the severity of their condition. Regular follow-up appointments with your vet will help monitor progress after treatment and allow you to observe any changes in behavior or symptoms.







