Cats have been captivating us for centuries with their grace, beauty, and mysterious personalities.
But have you ever wondered what’s beneath their soft fur and adorable meows? Specifically, have you ever wondered what a cat’s skull looks like?
Believe it or not, a cat’s skull is an incredible piece of anatomy that has evolved over time to help them hunt and survive. The cat’s skull is a complex structure made up of several important features such as nasal bones, eye sockets, jaws, and the cranial cavity.
Each component plays a vital role in the cat’s ability to see, smell, and locate prey. It’s fascinating to think about how cats have evolved over hundreds of thousands of years to develop such unique hunting skills.
In this blog series, we’ll delve into the intriguing world of cat skulls. We’ll explore the distinctive features that make a cat’s skull so special and compare it to other feline species.
We’ll also take a look at how the cat’s skull has changed over time to become the impressive structure it is today. Whether you’re a devoted cat lover or simply curious about the natural world around us, this blog series is sure to captivate your interest.
So, let’s find more.
Anatomy of a Cat’s Skull
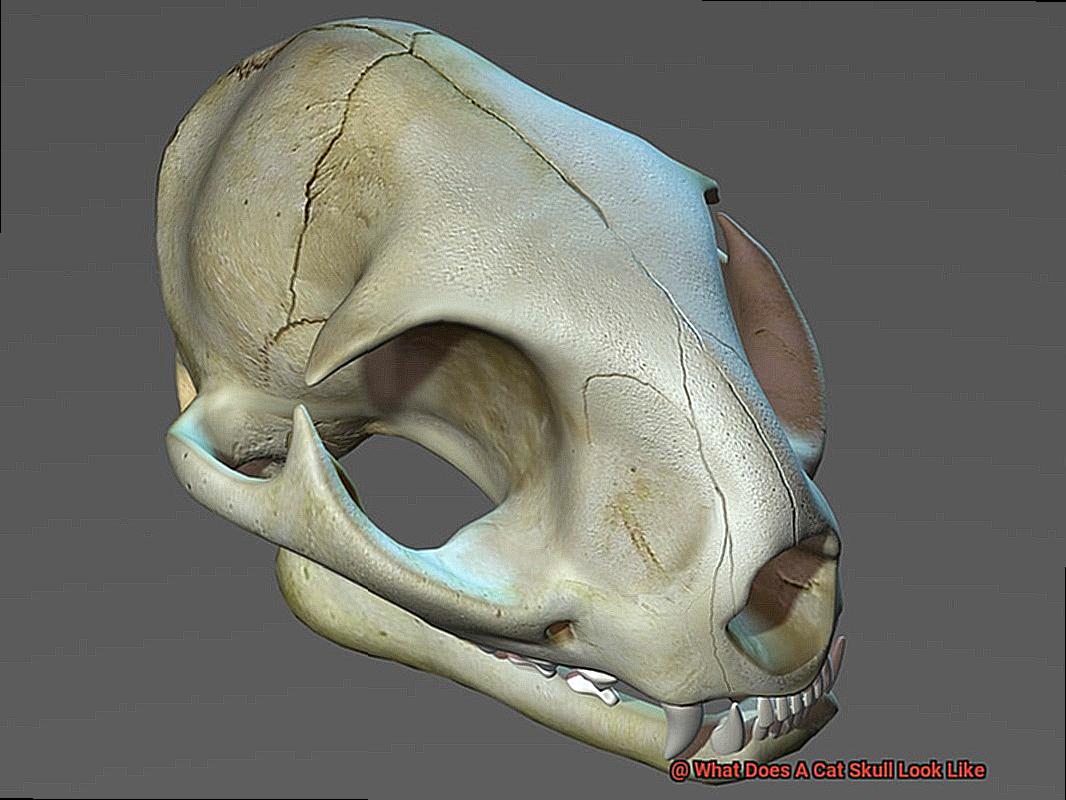
The anatomy of a cat’s skull is a marvel of nature, with intricate features that serve various functions.
Composed of several fused bones, a cat’s skull creates a robust structure that protects its brain and facilitates efficient jaw movement. One of the most distinctive features of a cat’s skull is its elongated snout.
This snout houses the cat’s sharp teeth and sensitive whiskers, which are crucial for their hunting skills. But that’s not all; the nasal cavity also plays a pivotal role in their sense of smell, which is incredibly powerful and able to detect odors beyond human comprehension.
A cat’s skull also boasts large eye sockets that provide them with exceptional peripheral vision and depth perception. Their eyesight is so sharp that they can detect even the slightest movements, making them successful hunters.
But what about their hearing? Cats have an extraordinary auditory system, thanks to their cone-shaped ears that are positioned high on the skull.

These ears allow them to pick up even the faintest sounds in their environment. The bones in their middle ear are also unique, amplifying sound vibrations and enabling them to hear higher frequencies than humans.
Understanding the anatomy of a cat’s skull is crucial for their overall wellbeing. Proper dental care is essential since their teeth play such a vital role in their health and ability to hunt.
Shape of the Skull
It’s truly a remarkable feature that sets them apart from other animals.
The shape of a cat’s skull is both functional and aesthetically pleasing, making it a defining characteristic of these incredible creatures. To begin with, a cat’s skull is relatively small compared to its body size, and it’s shaped like a wedge.
This unique shape allows for the cat’s eyes to be positioned on the front of its face, providing exceptional depth perception and binocular vision. As a result, cats can detect even the slightest movements in their environment and see objects in three dimensions better than humans.
Moreover, the rounded shape of the skull is due to the presence of the braincase that houses, protects and supports the cat’s brain. This critical feature ensures that the brain is safeguarded against injuries while the cat goes about its daily activities.
But wait, there’s more. The nasal cavity of a cat’s skull is relatively large compared to its body size, allowing for more air to pass through and more receptors to pick up scent molecules.
This incredible sense of smell is why cats have an excellent ability to detect changes in their environment and are often used for search and rescue missions. Aside from their functional benefits, the shape of a cat’s skull also has aesthetic value.
The sleek lines and elegant curves of their skulls are often admired for their beauty and grace. Artists and designers have been inspired by this stunning feature for centuries, incorporating it into their work as a symbol of sophistication and elegance.
From their exceptional vision to their keen sense of smell and stunning appearance, every aspect of their skull plays an important role in their lives.

Nasal Bones and Nostrils
These intricate features are crucial for a feline’s olfactory skills, and I am here to enlighten you on the wonders of their nasal bones and nostrils.
Located at the front of their skull, the nasal bones form the bridge of a cat’s nose, providing vital support for the delicate cartilage that makes up the rest of their nose. Although small in comparison to other animals, these nasal bones aid in detecting even the faintest scents and distinguishing between them.
The nostrils, also known as nares, are relatively small but wide enough to allow for efficient airflow. What’s more, these nostrils can move independently from each other, allowing cats to control their sense of smell and pinpoint the exact source of an odor.
But wait, there’s more. Cats have an additional organ called the vomeronasal organ located in the roof of their mouth.
Together, these characteristics make up a cat’s incredible sense of smell, which is highly developed and essential for their survival.
Eye Sockets
These features are not just mere indentations on a skull.
They play a crucial role in a predator’s survival, and I’m excited to share with you some new insights into their anatomy and function. Firstly, the size of a cat’s eye sockets is no coincidence.
Felines rely heavily on their eyesight to stalk prey. The sockets’ large size provides a wider lens, allowing for greater vision and depth perception.
Imagine having a panoramic view of your surroundings – that’s what a cat sees. But wait, there’s more.
The circular shape of the sockets and the bony ridge above them are unique to cats. This ridge acts as a shield, protecting the eyes from potential harm while still anchoring the muscles that control eye movement.
It’s like having a built-in fortress for those precious eyes. And let’s not forget about the third eyelid, also known as the nictitating membrane.
This translucent membrane is present in cat skulls and serves as an undercover weapon. It swiftly moves across the eye to protect it from dust, debris, and other potential hazards.
It also helps keep the eye moist, ensuring clear vision at all times. In summary, a cat’s eye sockets are marvels of nature, designed specifically for the needs of a predator.

Dental Formula of Cats
Think of a dental formula as a blueprint for your cat’s teeth.
It tells us how many teeth they have and what type they are. In total, cats have 30 teeth in their mouths, and each one serves an essential purpose.
Let’s break it down a bit further. The first set of numbers (I 3/3) refers to the incisors.
These are the small teeth located at the front of their mouth that help cats grasp and hold onto their prey. With three incisors on each side of their upper and lower jaws, cats have a total of six incisors in their mouth.
The second set of numbers (C 1/1) refers to the canines. These are the longer, pointed teeth situated next to the incisors.
Canines aid cats in tearing through bones and tough skin. With one canine on each side of their upper and lower jaws, cats have a total of four canines.
The third set of numbers (P 3/2) refers to the premolars. These teeth sit next to the canines and are responsible for separating meat and crushing bones.
Cats have sixteen premolars in total, with three on each side of their upper jaw and two on each side of their lower jaw. The final set of numbers (M 1/1) refers to the molars, which are located at the back of their mouth.
Molars help cats grind their food before swallowing. Cats have four molars in total, with one on each side of their upper and lower jaws.
Knowing your cat’s dental formula is vital for maintaining good oral hygiene. Regular dental checkups and cleanings can help prevent dental issues such as gum disease, tooth decay, and even tooth loss.
Braincase Structure
The braincase of a cat’s skull is a complex and crucial structure that deserves our attention and admiration.
Acting as a fortress, it houses and protects the brain, inner ear, and other vital organs of the head. Comprised of several fused bones, including the frontal, parietal, occipital, and temporal bones, the braincase forms a protective shell around the brain.
The frontal bone forms the forehead and eye sockets, while the parietal bone forms the top and sides of the braincase. The occipital bone forms the back of the skull and base of the braincase, while the temporal bone contains the ear canal.
Interestingly, different breeds of cats have unique skull shapes and sizes that reflect their individual characteristics. Some have flatter skulls while others have more rounded ones.
Larger cats tend to have larger brains and consequently larger braincases to accommodate their bigger heads. Imagine the braincase as a superhero’s shield, keeping sensory organs like sight and hearing functioning correctly while safeguarding the delicate structures inside.
SogRHPEuVG4″ >
Conclusion
In conclusion, a cat’s skull is a marvel of nature, intricately designed to aid in their hunting and survival.
From their keen sense of smell to their exceptional vision, every component of the skull plays a vital role in their lives. The unique shape of a cat’s skull not only serves a functional purpose but also adds to their stunning appearance.
It’s no wonder they are often admired for their beauty and grace. To ensure our feline friends’ overall wellbeing, it’s crucial to understand the structure and function of their skull.
Proper dental hygiene is essential for their ability to hunt and thrive. By appreciating the unique features of a cat’s skull, we can provide them with the care they need to live happy and healthy lives.
In short, the cat’s skull is not just an ordinary part of its body; it is an intricate system that has evolved over time to make them successful hunters.

