Are you concerned about your furry feline’s well-being?
As a devoted cat parent, it’s natural to want your pet to be healthy and content. Monitoring your cat’s heart rate is one of the most critical things you can do to ensure its overall health.
After all, a cat’s heart rate can provide valuable insight into its condition. Did you know that cats have significantly higher heart rates than humans?
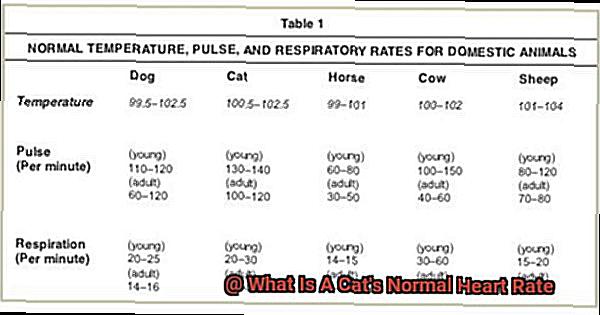
A cat’s heart rate can range from 140 to 220 beats per minute (BPM), which is much faster than our average of 60 to 100 BPM. Knowing what constitutes a normal range for a cat’s heart rate is essential because any deviation from this range could be indicative of an underlying health issue.
In this article, we’ll delve into everything you need to know about your cat’s heart rate. We’ll cover what factors can impact it, how to monitor it, and what steps you should take if you notice any abnormalities.
So sit tight, relax, and let us guide you through everything there is to know about your cat’s heart rate.
Understanding a Cat’s Heart Rate
One crucial aspect of this is understanding your cat’s heart rate.
A normal heart rate for a healthy adult cat usually ranges between 140 to 220 beats per minute (bpm), but this may vary depending on factors such as age, breed, and activity level. Kittens and senior cats may have slightly higher or lower heart rates compared to adult cats.
To measure your cat’s heart rate, you can place your hand on its chest and count the number of beats in 15 seconds, then multiply that number by four to get the bpm. Alternatively, you can use a stethoscope to listen to your cat’s heartbeat directly.
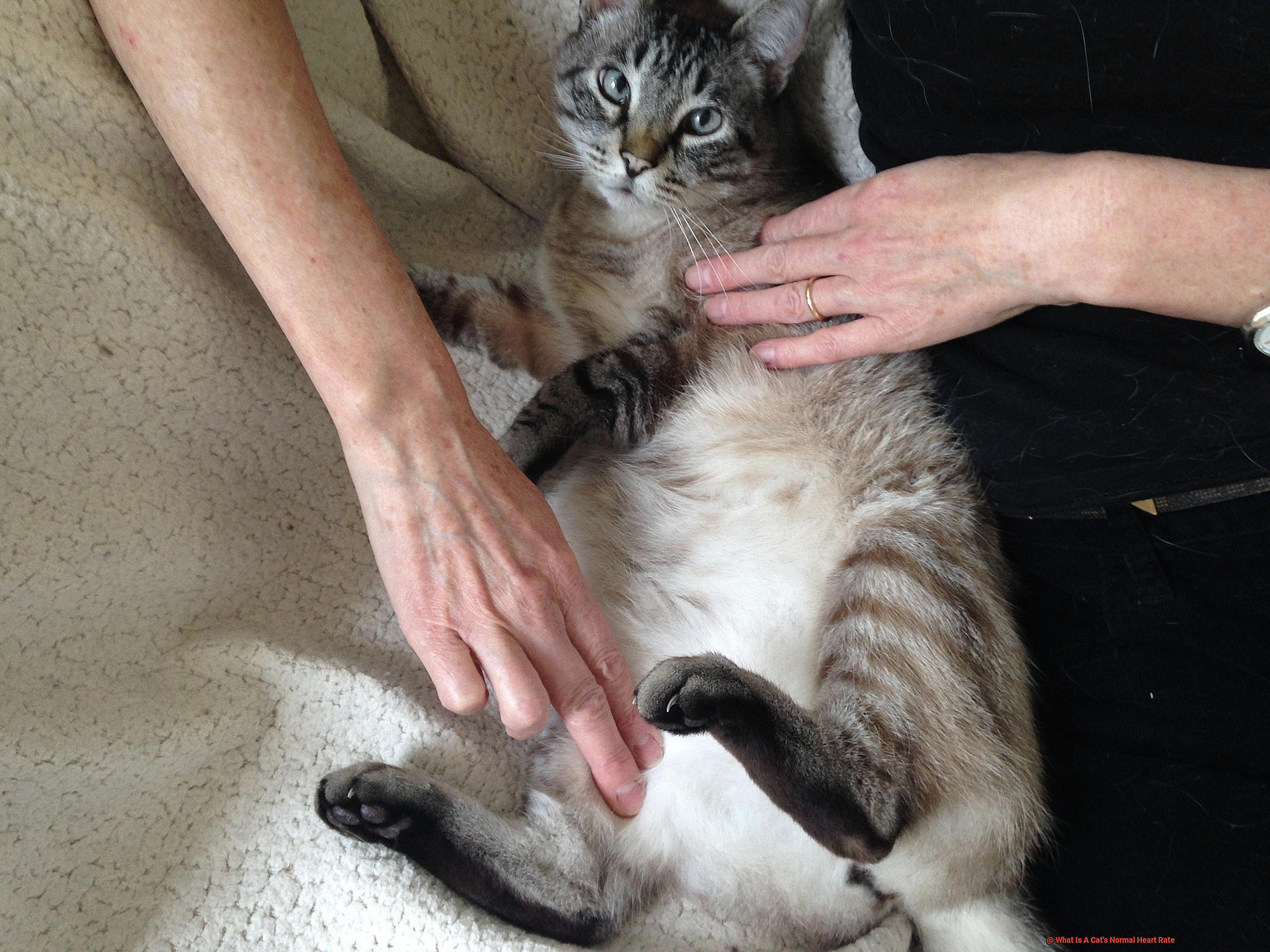

Regularly monitoring your cat’s heart rate will help detect any potential health issues early on. A high or low heart rate in cats could be an indication of underlying medical conditions such as hyperthyroidism, heart disease or stress.
It’s essential to consult with your veterinarian if you notice any abnormalities in your cat’s heart rate. Early detection of these issues can ensure that your cat receives proper diagnosis and treatment.
Average Resting Heart Rate of an Adult Cat
A vital part of that is keeping track of their heart rate, which typically ranges from 140 to 220 beats per minute (BPM) when at rest.
However, it’s important to remember that several factors can influence this range, such as age, weight, breed, and activity level. To accurately measure your cat’s resting heart rate, it’s crucial to ensure they’re relaxed and not stressed.
You can accomplish this by petting them softly or providing them with their favorite treats. Then, place your hand on their chest or feel for their pulse on their inner thigh.
Count the number of heartbeats you feel in 15 seconds and multiply that number by four for the BPM. Bear in mind that a cat’s heart rate can increase due to stress or excitement.
Therefore, it would be best to measure their heart rate when they’re calm. An abnormal heart rate may indicate underlying health issues such as hyperthyroidism or heart disease.
If you notice any unusual changes in your cat’s heart rate or behavior, it’s best to consult with your veterinarian as soon as possible.
Variations in Heart Rate Based on Breed and Age
Firstly, let’s talk numbers. An adult cat’s heart rate typically ranges from 140 to 220 beats per minute.
However, kittens have faster metabolisms and require more blood pumping to support their growth and development, resulting in higher heart rates ranging from 200 to 260 bpm. Secondly, breed plays a role in a cat’s heart rate.
Some breeds are known for having higher or lower heart rates than others. For example, the Siamese breed often has a higher heart rate than other breeds, while the Persian breed tends to have a slightly lower heart rate.
Knowing your cat’s breed can help you determine whether their heart rate is within a healthy range or not.
Thirdly, age is another factor that can affect a cat’s heart rate.
As cats get older, their bodily functions slow down, which can cause a slight decrease in their heart rate. However, significant changes in your cat’s heart rate should always be discussed with a veterinarian.
Finally, external factors such as stress or anxiety can also impact your cat’s heart rate. If your cat is feeling anxious or stressed, their heart rate may increase.
Conversely, if they are relaxed and resting, their heart rate may be lower than usual. In conclusion, understanding the normal range of your cat’s heart rate based on their breed and age is crucial for keeping them healthy and happy.
Remember to consult with your veterinarian if you notice any concerning changes.
The Significance of Monitoring a Cat’s Heart Rate
One crucial aspect of this is monitoring their heart rate regularly.
Not only can a cat’s heart rate fluctuate based on their unique traits such as age, breed, and size, but external factors like stress or physical activity can also play a role. Therefore, it’s important to keep a close eye on their heart rate under normal conditions when they are calm and relaxed.
A healthy cat’s heart rate typically ranges between 140-220 beats per minute (bpm). However, this can vary depending on their characteristics.
For instance, kittens and smaller cats tend to have higher heart rates than adult cats and larger breeds. It’s essential to know your cat’s baseline heart rate range to detect any abnormalities early on.
Regular monitoring of your cat’s heart rate can help identify underlying health issues such as heart disease or respiratory problems. If you consistently observe that your cat’s heart rate is outside the normal range, seek veterinary attention immediately.
Fortunately, monitoring your cat’s heart rate at home is relatively easy. You can use a stethoscope to listen to their heartbeat by placing it on the left side of their chest, just behind the elbow.
Alternatively, you can feel their pulse on the inside of their thigh or by placing your hand over their chest. It’s important to note that external factors such as stress, excitement, or physical activity can also affect a cat’s heart rate.
Potential Health Issues Related to Abnormal Heart Rates
One of the most important things you can do is monitor their heart rate.
Abnormal heart rates in cats are often an indication of underlying health issues that require immediate attention. Let’s dive deeper into potential health issues linked to abnormal heart rates in cats.
Heart disease is a common cause of irregular heart rates in cats. This disease can cause an arrhythmia or irregular heartbeat.
Symptoms may include difficulty breathing, lethargy, and poor appetite. If you notice any of these symptoms, it’s essential to seek veterinary care immediately.
High blood pressure, also known as hypertension, is another potential health issue that can cause abnormal heart rates in cats. Kidney disease or other underlying health issues may cause this condition.
If you leave high blood pressure untreated, it can lead to serious complications like blindness and kidney failure. Respiratory problems such as asthma or chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) can also cause labored breathing and increased heart rate in cats.
These conditions may be triggered by environmental factors such as dust or smoke or may be related to allergies. Thyroid issues such as hyperthyroidism can also lead to abnormal heart rates in cats.
This condition is caused by an overactive thyroid gland and can lead to weight loss, increased appetite, and hyperactivity. If your cat experiences a rapid heart rate or palpitations along with symptoms like fainting or weakness, it could be a sign of a severe condition like hypertrophic cardiomyopathy.
In such cases, immediate medical attention is crucial. Regular checkups with a veterinarian are vital for maintaining your cat’s overall health and well-being.
Your vet can perform routine screenings to detect any potential health issues early on and provide appropriate treatment. In conclusion, being aware of your cat’s normal heart rate and potential health issues related to abnormal heart rates helps ensure your cat stays healthy and happy.
If you notice any concerning symptoms or changes in your cat’s behavior, don’t hesitate to seek veterinary care immediately.
Tips for Monitoring Your Cat’s Heart Rate
By doing so, you can detect any potential issues early on and seek veterinary attention if necessary. In this article, we will explore seven tips for monitoring your cat’s heart rate.
Understanding a Cat’s Normal Heart Rate
Before you start monitoring your cat’s heart rate, it’s important to understand what a normal heart rate is. Generally, a cat’s heart rate should be between 140 and 220 beats per minute (BPM). However, keep in mind that this can vary depending on factors such as age, breed, and overall health. By understanding your cat’s normal heart rate, you can monitor their cardiovascular health more effectively.
There are several ways to monitor your cat’s heart rate at home.
Use a Stethoscope
One way is to use a stethoscope to listen to their heartbeat. This will give you a more accurate reading and allow you to listen for any irregularities or abnormalities in their heartbeat. Another option is to feel for their pulse by placing your fingers on their inner thigh or underneath their front leg.
Count the number of beats you feel within 15 seconds and multiply that number by four to get their heart rate in BPM. You can also use a pulse oximeter, which attaches to your cat’s paw or ear and measures its heart rate and oxygen levels.
Monitoring Your Cat’s Heart Rate During Stressful Situations
It’s important to monitor your cat’s heart rate during stressful situations, such as during playtime or when visiting the vet.
If you notice that their heart rate is consistently outside of the normal range, it may be time to consult with your veterinarian to rule out any underlying health issues.
Paying attention to your cat’s heart rate during these situations can help ensure that they stay healthy and happy
Cardiovascular Issues in Cats
In addition to monitoring your cat’s heart rate, it’s important to keep an eye out for other signs of cardiovascular issues.
Difficulty breathing, coughing, or a bluish tinge to their gums or tongue could be a sign of a serious heart issue and should be addressed immediately.
By keeping an eye out for these signs, you can help catch any potential issues early on.
Regular Check-Ups
Regular check-ups with your veterinarian can help ensure that your cat’s heart rate remains within a healthy range and any potential issues are detected early on.
Your vet can also provide you with tips on how to monitor your cat’s heart rate at home and answer any questions you may have.
By staying on top of your cat’s cardiovascular health, you can help ensure that they live a long and healthy life.
Factors That Can Affect Your Cat’s Heart Rate
Age and Breed
The age and breed of your cat can play a significant role in determining its heart rate.
For example, kittens tend to have a higher heart rate than adult cats, with an average range of 200-260 bpm. As cats age, their heart rate typically decreases, with senior cats having a lower heart rate than younger cats.
Additionally, certain breeds may have a naturally higher or lower heart rate due to genetic factors. For instance, the Siamese breed is known for having a higher heart rate than other breeds.
It’s essential to keep these factors in mind when monitoring your cat’s heart rate to ensure that any changes are not due to natural variations.
Activity Level
Physical activity can also affect your cat’s heart rate.
When your cat is active, their heart rate will increase to meet the increased demand for oxygen and nutrients in its body. Conversely, when they are resting or sleeping, their heart rate will decrease as their body requires less energy.
Monitoring your cat’s heart rate during different activities can help you determine what is normal for them and identify any potential issues.
Stress and Anxiety
Stressful situations such as loud noises, unfamiliar environments, or changes in routine can cause an increase in your cat’s heart rate.
Similarly, anxiety or fear can also cause an elevated heart rate. It’s important to monitor your cat’s heart rate during these situations to ensure that it returns to normal once the stressor has passed.
If your cat’s heart rate remains high even after the stressor has been removed, it may be a sign of an underlying health issue.
Health Conditions
Several health conditions can affect your cat’s heart rate, including hypertrophic cardiomyopathy (HCM), hyperthyroidism, and respiratory issues such as asthma.
HCM is a common heart condition in cats that causes the walls of the heart to thicken, leading to an irregular heartbeat and potentially life-threatening complications. Hyperthyroidism is a condition where the thyroid gland produces too much hormone, leading to an increased heart rate.
Respiratory issues such as asthma can also cause an elevated heart rate due to difficulty breathing. It’s essential to monitor your cat’s heart rate regularly and seek veterinary care if you notice any abnormalities or symptoms of these conditions.
Conclusion
In conclusion, keeping a close eye on your cat’s heart rate is an essential part of responsible pet ownership.
As a loving cat parent, it’s crucial to know what constitutes a normal heart rate for your feline friend and to be aware of any deviations from this range. Typically, a healthy adult cat’s heart rate falls between 140 to 220 beats per minute (BPM), but this can vary based on factors such as age, breed, and activity level.
Regularly monitoring your cat’s heart rate can help detect potential health issues early on. Any abnormalities in their heart rate could indicate underlying medical conditions like hyperthyroidism or heart disease.
In such cases, seeking veterinary attention is vital if you notice any concerning changes in your cat’s behavior or heart rate. Luckily, there are various ways to monitor your cat’s heart rate at home using a stethoscope or feeling for their pulse.
By following these simple tips and staying vigilant about your furry companion’s cardiovascular health, you can ensure that they receive the love and care they deserve.

